SMART-Control
Smart framework for real-time monitoring and control of subsurface processes in managed aquifer recharge applications

Partners
Partners
INOWAS research group, Department of Hydrosciences, Technische Universität Dresden
Berlin Centre of Competence for Water (KWB)
Umwelt- und Ingenieurtechnik GmbH Dresden (UIT)
Adelphi research gGmbH
French Geological Survey (BRGM)Alexandre Duzan
Lyonnaise des Eaux/Suez
Universidade Federal de Paraíba (UFPE)
Universidade Federal de Pernambuco (UFPB)
University of Cyprus (UCY)
Abstract
Abstract
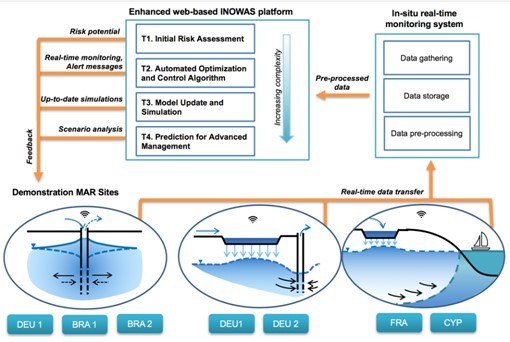
The main objective of the SMART-Control project is to reduce the risks in the application of sustainable groundwater management techniques worldwide through the development and implementation of an innovative web-based, real-time monitoring and control system (RMCS) in combination with risk assessment and management tools (RAM). Managed aquifer recharge (MAR) represents an efficient water reuse technique to restore groundwater-dependent ecosystem services. Despite its wide benefits, the contribution of MAR to safe water supply at global scale is still limited. The reasons include lack of data on MAR technological costs, hydrogeological site-specific characteristics, the associated risks with operational challenges and the lack of national regulations. The lack of detailed and up-to-date monitoring data hinders the reliable setup and calibration of numerical models for risk assessment in nature-based systems such as MAR facilities. The implementation of RMCS will not only enable the assessment and management of risks at MAR sites but also decrease the uncertainties in numerical models. The SMART-Control framework consists of a cloud-based monitoring and modelling framework for real-time, web-based groundwater management where time series data collected from sensor networks installed at selected MAR sites will be remotely transferred and automatically fed into real-time simulation-optimization algorithms. The proposed system will include three main components: 1) in-situ real-time monitoring system consisting of sensors installed on-site coupled with pre-processing algorithms; 2) web-based modelling and monitoring platform including automated optimization and control algorithms, model update tool to incorporate real-time data into numerical flow and transport models and a prediction tool to involve climate change and water demand scenarios and 3) a set of RAM tools to evaluate MAR-associated risks. This smart innovative framework for MAR (SMART-Control) will allow for real-time control and risk assessment of MAR facilities at any stage of development so that implementation, management and operational capabilities are improved. In addition, the development of risk assessment guidelines for the application of MAR ensures that the implementation of the solution is supported by a legal framework. The approach will be tested at six MAR sites (pilot to full-scale) in Germany, France, Brazil and Cyprus. Each case study represents a different MAR setting in terms of infiltration method, boundary conditions, objectives, quality and quantity of recharged and recovered water, operational scheme, as well as technical and ecological constraints. The variety of case studies ensures that the SMART-Control framework can be applied to various environmental and operational conditions to promote and improve the integrated water resources management techniques. The approach will thus bring real-time evidence that despite MAR is a nature-based solution, risks associated with the implementation and operation can be managed and controlled and demonstrates that it is a safe and reliable technique for integrated water resources management.The international consortium consists of nine full partners comprised of four universities, three research institutes and two companies. Additionally, associated partners involving water works, water managers and stakeholders in the participating countries support the project and benefit directly from the project outcomes.
Project structure:
Project structure:
WP1: Project Management
WP2: Integrated framework for assessing and managing MAR-associated risks and benefits
WP3: In-situ real-time observation system
WP4: Development of web-based monitoring and modelling platform for real-time control and risk assessment
WP5: Demonstration of approach and developed tools
WP6: Training in the use of SMART-Control software
WP7: Strengthening the SMART-Control approach
Outcomes and expected impact:
Outcomes and expected impact:
The main outcome of SMART-Control will be the development of an innovative web-based open source platform including modelling, monitoring and risk assessment tools to improve the management and operation of MAR facilities and reduce the associated risks. The web-based platform will include various tools for monitoring, modelling and risk assessment of MAR facilities. The first tool (T1) aims at initial risk assessment with the evaluation of risks and remediation measures which will be published in guidelines. The second tool (T2) will be developed as a guided instrument to evaluate subsurface removal processes of pathogens. The tool will incorporate real-time monitoring data in combination with automated optimization and control algorithms and will be integrated on the web-based platform. In addition, real-time monitoring data will be utilized for up-to-date optimisation and management simulations based on the numerical modelling scheme of the MAR system (T3). With the help of the prediction and advanced management tool (T4), upcoming changes regarding climate change and urban development can be incorporated into the modelling framework. The developed tools span various complexities (literature guidelines to numerical modelling and prediction) to cover the demand at a wide range of facilities and will be tested at six MAR plants. A guideline on the transfer of the SMART-Control approach including a cost-benefit analysis (CBA) and a technological transfer concept will be published allowing system operators to quantify the site-specific benefits of the implementation of an advanced monitoring and control concept. Besides the publication of guidelines, the results of SMART-Control will be presented at international conferences and will be published in at least two open access articles. In addition, training material will be developed including web-based documentation pages and online user-guides for the various features of the web-based platform. Workshops in the participating countries and webinars will be established to increase the user circle of the web-based platform and facilitate its application. Increased monitoring frequency of microbial, operational and chemical parameters using online tools increases the safety of water production and the data density for process performance validation and provides cost-effectively relevant information for MAR operations. SMART-Control will prove that despite MAR is a nature-based solution, risks associated with the implementation and operation can be managed and controlled and demonstrates that it is a safe and reliable technique for integrated water resources management. The web-based platform offers a new scientific approach to analyse the relevant processes in real-time which enables the up-to-date diagnostic for operators, regulators and water managers. The SMART-Control project addresses key elements of the JPI Water RDI agenda by facilitating international cooperation among four European and one non-European partner, fostering the implementation of related international & EU policies and promoting transdisciplinary research among researchers and end-users to enhance the efficient and sustainable use of water resources under the impact of climate change. The main added-value of the project is on bridging the gap in “water supply-demand” paradigm through technological innovation, rising social awareness, improvement of ecosystem services, demonstrating economic viability and integration of policies. The measures proposed contribute to SDGs 6, 11 and 13 by promoting and ensuring safe water supply and sustainable management, and by making cities more resilient and sustainable in the combat with climate change and its impact. The project builds on previous as well as on-going European, national and bilateral projects. The web-based monitoring and modelling platform developed within the BMBF-funded Junior Research Group INOWAS (#01LN1311A) will be extended and will incorporate and further enhance tools implemented within the projects AquaNES (#689450), SubSol (#642228), DEMEAU (#308339) and DEMOWARE (#619040). The international consortium, consisting of nine full partners from Germany, France, Brazil and Cyprus and several associated partners composed of stakeholders and end-users, promotes the international cooperation which allows the achievement of project results that would otherwise not be possible. The participation of stakeholders and end-users is ensured during the whole project lifetime through the participation in project meetings and training activities to maximise the dissemination of project results. SMART-Control supports young researchers and entrepreneurs by producing open source and free software to promote digital education and jobs, avoiding the creation of barriers or inequalities often caused by high license fees. The project aims to create a trans-disciplinary environment for researchers by bringing together water scientists, water managers, economists and software developers. Additionally, an Advisory Board consisting of two experts with high international reputation on MAR assessment will ensure the quality control of project activities.