FOREWARN
Development of a smart forewarning system to assess the occurrence, fate and behaviour of contaminants of emerging concern and pathogens, in waters
Partners
Partners
University of Helsinki (UH)
French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety (ANSES)
Dublin City University (DCU)
Attikon University Hospital (UA)
Abstract
Abstract
FOREWARN will assess the occurrence, fate and behaviour of contaminants of emerging
concern (CECs) and pathogens, and develop machine-learning methods to model their transfer and behaviour and build a decision support system (DSS) for predicting risks and propose mitigation strategies. FOREWARN will be focussed on CECs such as antibiotics and pathogens such as antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB), antibiotic resistance genes (ARG) and emerging viruses, such as SARS-CoV-2.
Using large datasets from previous research, FOREWARN will establish the basis of the relationships between the conditions of a particular aquatic environment such as the hydrological and geological conditions, clime, drought and floods, the anthropogenic stressors such as water supply, wastewater discharges, type of wastewater discharges, among many others, and the emerging pollution that is CECs and emerging pathogens.
The project will consider 2 types of case studies:
1. In-silico case studies will be selected from previous results and dataset obtained in past or ongoing EU projects. Data will be used to develop the models and algorithms to feed and develop the DSS system to better understanding the sources, transport, degradation of CECs and pathogens and modelling their behaviour.
2. The adaptive DSS system will be refined and tested under real environmental conditions to achieve TRL5 in real environment case studies.
WP structure
WP structure
WP number | Led by |
| WP1 | IDAEA-CSIC |
| WP2 | UA |
| WP3 | DCU |
| WP4 | ANSES |
| WP5 | IDAEA-CSIC |
| WP6 | IDAEA-CSIC |
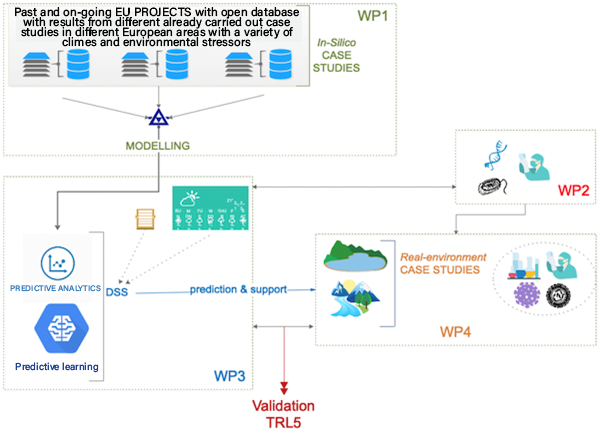
Expected research results
Expected research results
- Occurrence fate and behavior of CECs and pathogens of case study areas.
- Machine-learning methods to model CESs and pathogens transfer and behavior, and a decision support system (DSS) for predicting risks and propose mitigation strategies.